What is environment in Apigit test tool
Apigit's environment is a feature that allows you to create and manage different sets of variables that can be used in your requests. An environment can be thought of as a collection of key-value pairs that can be accessed and modified within Apigit.
In simpler terms, an environment is a way to store variables such as URLs, access tokens, and other values that are frequently used in your API requests. By storing these values in an environment, you can easily switch between different configurations and run your requests against different environments without manually updating the values each time.
Each environment in Apigit consists of a set of variables, including global variables that can be accessed by all requests in the workspace, and environment-specific variables that are only available to requests within that environment. Variables can be set and updated manually, or they can be set dynamically using scripts or the Apigit API.
You can create multiple environments within a Apigit workspace, and easily switch between them using the environment dropdown menu. This makes it easy to test your API against different environments, such as development, staging, and production, without having to manually update your requests each time.
Create your first environment set
When debugging an API, we often need to switch back and forth between local, development, and production environments. We also face issues such as expired tokens, which can be frustrating. Some tutorials suggest using Apigit to simplify the process, but in practice, we may still encounter some problems. Therefore, this detailed blog post introduces the use of Apigit's Environments to simplify the steps of switching between different environments when debugging APIs seamlessly.
Steps to Use a Global Data Environment:
To edit your test case file, navigate to Test Cases within your repository and select the appropriate file. In the default view mode, click on the ✏️ icon located in the bottom left-hand corner of the sidebar.
To add or edit an environment set, click on the Env button located at the center of the top bar. From there, you can access the environment settings and make any necessary changes.
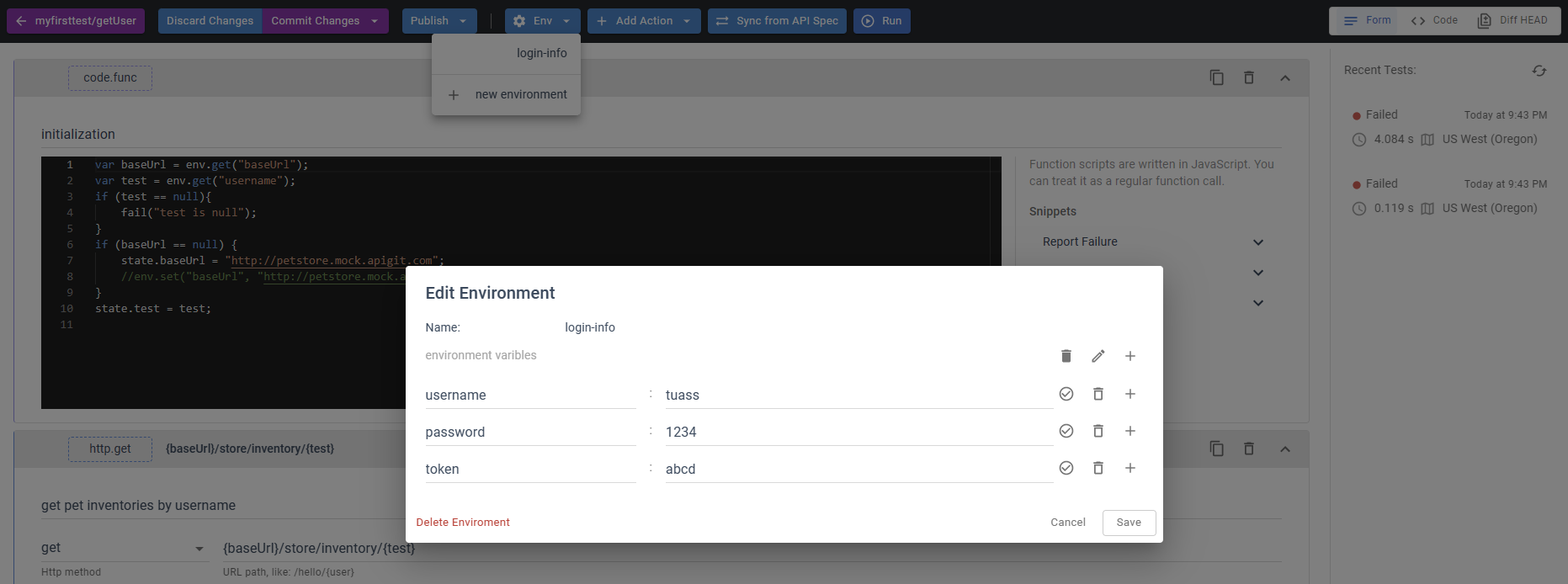
You have the option to switch between Code and Form view modes by clicking on the corresponding buttons located in the top right-hand corner of the page.
In Code mode:
[
{
"type": "code",
"description": "initialization",
"parameters": {
"code": "var baseUrl = env.get(\"baseUrl\");\nvar test = env.get(\"username\");\nif (test == null){\n fail(\"test is null\");\n}\nif (baseUrl == null) {\n state.baseUrl = \"http://petstore.mock.apigit.com\";\n //env.set(\"baseUrl\", \"http://petstore.mock.apigit.com\")\n}\nstate.test = test;\n"
}
},
{
"type": "http",
"description": "get pet inventories by username",
"parameters": {
"method": "get",
"url": "{baseUrl}/store/inventory/{test}",
"query": [],
"auth": {
"type": "{test}"
},
"header": [],
"body": {
"type": "none",
"data": ""
},
"postTest": "if (!res || res.status !== 200) {\n fail(\"get pet inventory failed\")\n}"
}
}
]
In Form mode:
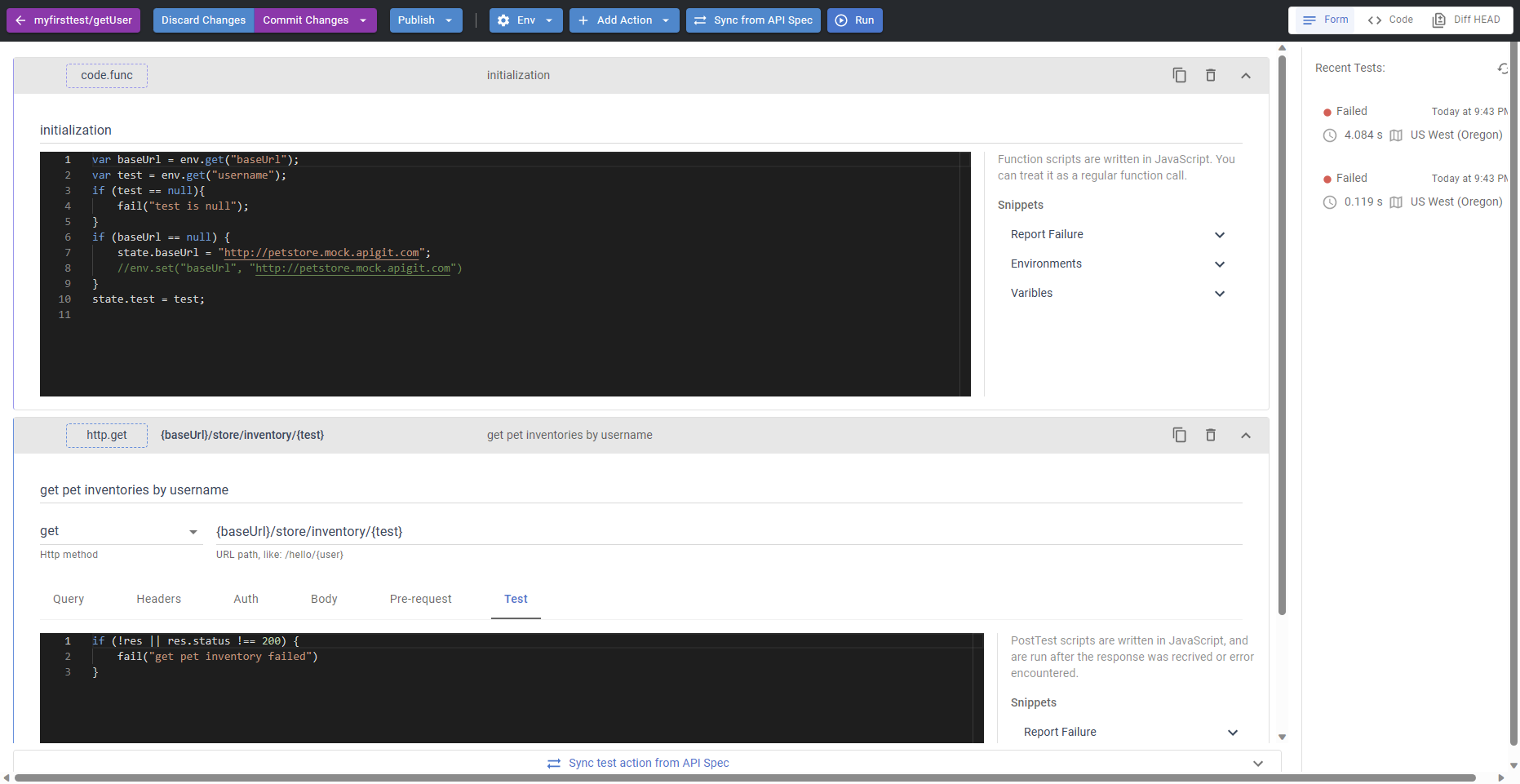
To use the environment data, you can add code in Code Execution Action or Test section of Http Request Action.
Note that the use of var is limited to its own section. If you define a variable, such as test, within section Code Execution Action and wish to use it within the HTTP Request Action section, you must use state.test to access the variable.
Related Posts
expressjs powered mockserver
Express.js powered mock servers provide flexible, customizable API simulations with dynamic responses, advanced routing, and middleware support for comprehensive testing and development environments.
explorer api testing
APIGit's testing tools enable developers to create, automate, and manage comprehensive test suites that validate API functionality, performance, and compliance with specifications.
automatic mockserver generation
Automatic mock server generation accelerates API development by instantly creating functional API simulations from OpenAPI specifications, complete with realistic example responses.
Ready to get started with APIGIT?
Join thousands of developers and teams who are already using APIGIT to streamline their API development workflow.